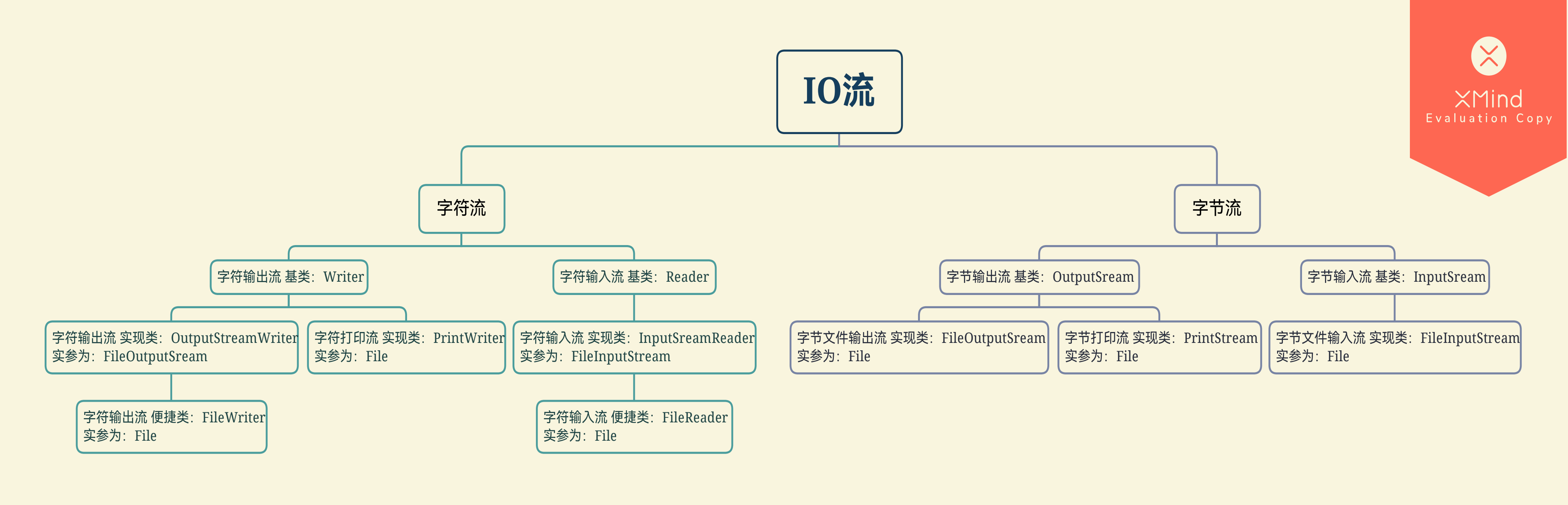
IO-进阶
案例
案例:复制单极文件夹
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建数据源目录
File srcFolder = new File("E:\\xiaobai");
//取数据源目录名字,不包括文件名
String srcFolderName = srcFolder.getName();
//新建目标目录
File destFoldername = new File(srcFolderName);
//如果没有目标目录,则创建
if (!destFoldername.exists()) {
destFoldername.mkdir();
}
//列出源文件目录下所有目标文件,加入File集合
File[] listFiles = srcFolder.listFiles();
for (File srcFile : listFiles) {
String srcFileName = srcFile.getName();//获取目标文件名
File destfile = new File(destFoldername, srcFileName);//拼接目标目录名和目标文件名
copyFile(srcFile, destfile);//调用方法复制文件
}
}
//复制文件方法
private static void copyFile(File srcFile, File destfile) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destfile));
byte[] by = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(by)) != -1) {
bos.write(by, 0, len);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
案例:复制多级文件夹
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File srcFile = new File("E:\\xiaobai");//源文件路径
File destFile = new File("F:\\");//目标文件路径
copyFolder(srcFile, destFile);//调用复制目录方法
}
private static void copyFolder(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException{
if (srcFile.isDirectory()) { //判断路径是否为目录,如果是,执行执行体内容
String srcFileName = srcFile.getName();//获取源路径下目录名
File newFolder = new File(destFile, srcFileName);//拼接新的目录名
//如果该目录不存在,则创建目录
if (!newFolder.exists()) {
newFolder.mkdir();
}
File[] fileArray = srcFile.listFiles();//获取源路径下所有目录/文件,创建File数组
for (File file : fileArray) {
copyFolder(file,newFolder);//递归调用复制目录方法!!!!!!!
}
}else {
//如果当前路径非目录,则获取文件名,拼接后调用复制文件方法
File newFile = new File(destFile, srcFile.getName());
copyFile(srcFile,newFile);
}
}
private static void copyFile(File srcFile, File file) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
byte[] by = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(by)) != -1) {
bos.write(by, 0, len);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
复制文件的异常处理
利用try catch处理
public class Demo09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("br.txt"));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("br.txt"));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (br != null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (bw != null) {
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
JDK7改进方案
在JDK7更新了try catch的新用法,格式为
try(定义流对象){
可能出现异常的代码
}catch(异常类名 变量名){
异常的处理代码
}
像是如上操作,不需要使用finally释放资源,会自动释放资源
public class Demo09_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("bw.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("br.txt"));) {
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
JDK9的改进方案
在这里,JDK9的方案就是把JDK7方案中的try()里面的定义拿到外面去做定义,但会出现方法仍需抛出异常的问题,所以JDK7的方案更靠谱一些