IO-流
IO流概述和分类
IO流分类:
- 按照数据的流向
- 输入流:读数据
- 输出流:写数据
- 按照数据类型来分
- 字节流:
- 字节输入流;字节输出流
- 字符流:
- 字符输入流;字符输出流
- 字节流:
一般来说,我们的IO流分类是按照数据类型来分的
- 如果数据通过windows自带的记事本打开,我们还可以读懂里面的内容,就是用字符流,否则使用字节流。如果你不知道该使用哪种类型的流,就用字节流
字节流
字节流写数据
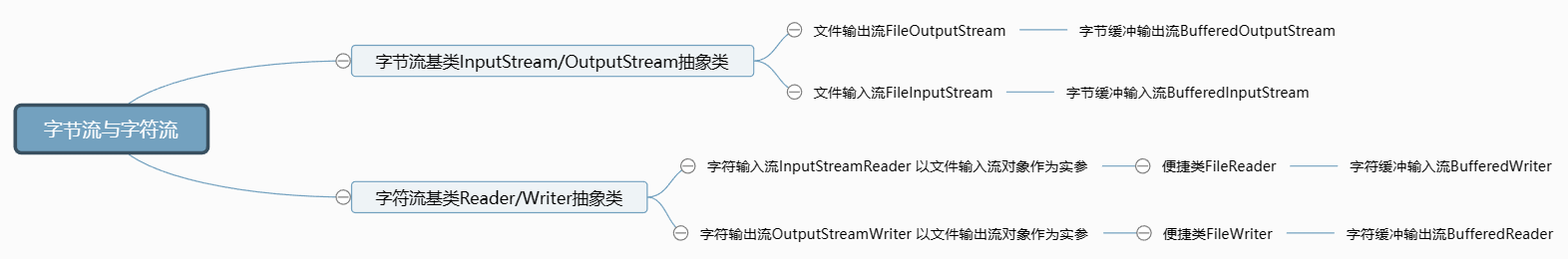
字节流抽象基类
- InputStream:这个抽象类是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类
- OutputStream:这个抽象类是表示字节输出流的所有类的超类
- 子类名特点:子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名的后缀
输入就是读,输出就是写
FileOutputStream:文件输出流 用于将数据写入File
- FileOutputStream(String name):创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件
使用字节流写数据的步骤:
-
创建字节流输出对象
-
调用字节输出流对象的写数据方法
-
释放资源(关闭此文件输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt");
fos.write(97);
fos.close();
}
}
字节流写数据的三种方式
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void write(int b) | 将指定字节写入此文件输出流,一次写入一个字节数据 |
| void write(byte[] b) | 将b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此文件输出流,一次写入一个字节数组数据 |
| void write(byte[] b,int off,int len) | 将len字节从指定的字节数组开始,从偏移量off开始写入此文件输出流,一次写一个字节数组的部分数据 |
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
byte[] bys = "abcde".getBytes();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt");
//fos.write(bys);//abcde
fos.write(bys,1,3);//bcd
fos.close();
}
}
字节流写数据的小问题:
字节流写数据如何实现换行呢?
- 写完数据后,加换行符
- windows: \r\n
- linux: \n
- mac: \r
字节流写数据如何实现追加写入呢?
- public FileOutputStream(String name,boolean append)
- 创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。如果第二个参数是true,则字节将写入文件的末尾而不是开头
字节流写数据加异常处理
finally:在异常处理时提供finally块来执行所有的清除操作。比如IO流中的释放资源
特点:被finally控制的语句一定会执行,除非JVM退出
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
byte[] bys = "abcde".getBytes();
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt");
//fos.write(bys);//abcde
fos.write(bys,1,3);//bcd
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
字节流读数据(一次读一个字节数据)
FileInputStream:从文件系统中的文件获取输入字节
- FileInputStream(String name):通过打开与实际文件的链接来创建一个FileInputStream,该文件由系统中的路径名name命名
使用字节输入流读数据的步骤:
- 创建字节输入流对象
- 调用字节输入流对象的读数据方法
- 释放资源
- 注:如果read方法读取到文件末尾将会返回"-1"
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("fis.txt");
// System.out.println(fis.read());
// System.out.println((char) fis.read());
//遍历文件中所有字节流
int by;
while ((by = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) by);
}
fis.close();
}
}
案例:复制文本文件
要求:复制字节流fis.txt到fos.txt中
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("fis.txt");
int by;
while ((by = fis.read()) != -1)
{
fos.write(by);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
字节流读数据(一次读一个字节数组数据)
read()方法中,读取一个字节数据时,括号内为空,表达式的值为数据内容(int)
读取一个字节数组内容时,read(b)方法中,括号里放字节数组,表达式的值为数据内容字节长度,读出数据放在字节数组里面
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("fis.txt");
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(b)) != -1)//实际读取长度不超过-1
{
System.out.println(new java.lang.String(b,0,len));
}
fis.close();
}
}
案例:复制图片
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("1.jpg");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("2.jpg");
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(b)) != -1){
fos.write(b,0,len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
字节缓冲流
buffer英文释义:缓冲器
-
BufferedOutputStream:该类实现缓冲输出流。通过设置这样的输出流,应用程序可向底层输出流写入字节,而不必为写入每个字节调用系统底层
-
BufferedInputStream:将创建一个内部缓冲区数组。当从流中读取或跳过字节时,内部缓冲区将根据需要从所包含的输入流中充数据,一次很多字节
构造方法:
- 字节缓冲输出流:BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
- 字节缓冲输出流:BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
为什么构造方法需要的是字节流,而不是具体的文件或者路径呢?
- 字节缓冲流仅仅提供缓冲区,而真正的读写数据还得依靠基本的字节流对象进行操作
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("bos.txt"));
bos.write("hello\r\n".getBytes());
bos.close();
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("bos.txt"));
//方法一:
int by;
while ((by = bis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) by);
}
//方法二:
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len= bis.read(b))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(b, 0, len));
}
bis.close();
}
}
注:字节流读数据时,fos.read()方法中如果没有参数,则读取一个数据,返回值为该数据的int类型assic码。如果参数为字节数组,则把数据写入到字节数组中,返回值为int类型的长度len
字符流
为什么会出现字符流
由于字节流操作中文不是特别的方便,所以JAVA提供字符流
- 字符流 = 字节流 + 编码表
字符流的底层仍然是字节流
汉字在存储的时候,无论是哪种编码,第一个字节都是负数
编码表
按照某一种规则,将字符储存到计算机中,叫做编码
反之,讲计算机中的二进制数按照某种规则解析显示,叫做解码
按照A编码存储,必须按照A编码解析,这样才能正常显示,否则会出现乱码
一套字符集必然存在一套字符编码,常见的字符集有:
- ASCII字符集
- GBXXX字符集
- GB2312:简体中文码表。包括7000个简体汉字
- GBK:最常见的中文码表。收录21003汉字,完全兼容GB2312标准。支持繁体中文和日韩汉字
- GB18030:最新的中文码表。收录汉字70244个,采用多字节编码,支持中国国内少数民族的文字
- Unicode字符集
- UTF-8:万国码
选用何种方法编码,必须选用何种方法解码
字符串的编码与解码
编码:
- byte[] getBytes():使用平台的默认字符集为String编码为一系列字节,将结果储存到新的字节数组中
- byte[] getBytes(String charsetName):使用指定的字符集将该String编码为一系列字节,将结果储存到新的字符数组中
解码:
- String(byte[] bytes):通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的字节数组来构造新的String
- String(byte[] bytes,String charsetName):通过指定的字符集解码指定的字节数组来构造新的String
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String s = "中国";
byte[] bys = s.getBytes("UTF-8");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bys));//[-28, -72, -83, -27, -101, -67]
byte[] bys1 = s.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bys1));//[-42, -48, -71, -6]
String s1 = new String(bys);
System.out.println(s1);//中国
String s2 = new String(bys1,"GBK");
System.out.println(s2);//中国
}
}
字符流的编码与解码
字符流抽象基类
- Reader:字符输入流的抽象类
- Writer:字符输出流的抽象类
字符流中编码解码相关类
- InputStreamReader(InputStream out,charsetName)
- OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out,charsetName)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//字符输出流以UTF-8的编码写入文件
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("osw.txt"),"UTF-8");
//字符输出流以GBK的编码写入文件
OutputStreamWriter osw1 = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("osw1.txt"),"GBK");
osw.write("中国");//中国
osw1.write("中国");//�й� 这里的乱码是因为idea平台的默认解码为UTF-8 使用GBK编码自然会乱码
osw.close();
osw1.close();
//字符输入流以默认(UTF-8)的方法解码读取文件
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("osw.txt"));
int ch;
while((ch=isr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)ch);//中国
}
isr.close();
System.out.println();
//字符输入流以GBK的方法解码读取文件
InputStreamReader isr1 = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("osw1.txt"), "GBK");
int ch1;
while((ch1=isr1.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)ch1);//中国
}
isr1.close();
}
字符流写数据的五种方式
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void write(int c) | 写入一个字符 |
| void write(char[] cbuf) | 写入一个字符数组 |
| void write(char[] cbuf,int off,int len) | 写入字符数组的一部分 |
| void write(String str) | 写入一个字符串 |
| void write(String str,int off,int len) | 写入字符串的一部分 |
| void flush() | 刷新流 |
| void close() | 关闭流(关闭前会刷新) |
注:字符流写数据之后,数据并不会直接写道文件中,需要用到flush()方法刷新。使用close()方法关闭流时会自动刷新一次
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("osw.txt"));
// osw.write(97);
// osw.flush();
// osw.write(98);
// osw.close();
// char[] chs = {'a','b','c','d','e'};
// osw.write(chs);//abcde
// char[] chs = {'a','b','c','d','e'};
// osw.write(chs,2,3);//cde
// osw.write("abcde");//abcde
osw.write("abcde",2,3);//cde
osw.close();
}
}
字符流读数据的两种方式
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| int read() | 一次都一个字符数据 |
| int read(char[] cbuf) | 一次读一个字符数组数据 |
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//一次读一个数据
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("osw.tx t"));
int ch;
while ((ch = isr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) ch);
}
isr.close();
//一次读一组数据
InputStreamReader isr1 = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("osw.txt"));
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len=isr1.read(chs)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(chs,0,len));
}
isr.close();
}
}
字符流读写的便捷类
当不需要改变字符集编码解码(即用平台默认的字符集)时,我们转换流可以用便捷类实现
- FileReader():继承自InputStreamReader()
- FileWriter():继承自OutputStreamReader()
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("osw.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWrit er("osw1.txt");
//方法一
int ch;
while ((ch = br.read()) != -1) {
bw.write(ch);
}
//方法二
char[] chr = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fr.read(chr)) != -1)
{
fw.write(chr,0,len);
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
}
字符缓冲流
构造方法:
- 字节缓冲输出流:BufferedWriter out(Writer out)
- 字节缓冲输出流:BufferedReader(Reader in)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("osw1.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("osw.txt"));
//方法一
int ch;
while ((ch = br.read()) != -1) {
bw.write(ch);
}
//方法二
int len;
char[] chs = new char[1024];
while ((len = br.read(chs)) != -1) {
bw.write(chs, 0, len);
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}
字符缓冲流特有功能
BufferedWriter:
- void newLine():写一行行分隔符,行分隔符字符串由系统属性定义
可以解决不同系统下行分隔符不同的问题
BufferedReader:
- public String readLine():读一行文字,结果包含行的内容的字符串
readLine读取数据时,返回一行数据为字符串,当返回为空时数据读完
注:readLine读数据时不包含换行符,需要在输出时操作
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("osw1.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("osw1.txt"));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
bw.write("hello" + i);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(br.readLine());
}
System.out.println(br.readLine());//NULL
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}
案例:复制文件
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("osw.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("osw1.txt"));
String str;
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();//readline不读取换行,需要额外写
bw.flush();//换行了就得刷新
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}